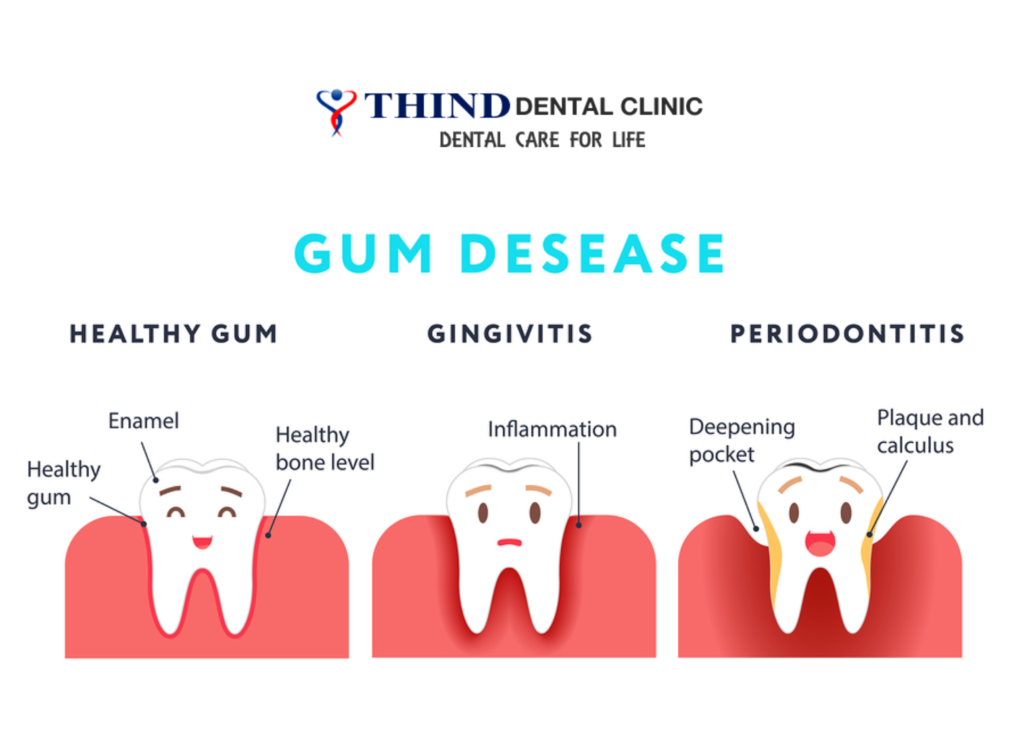
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, comprises two main stages: gingivitis and periodontitis. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and adopting preventive measures are vital for maintaining oral health and averting severe dental complications.
Symptoms:
- Gingivitis:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, particularly during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Changes in tooth alignment or partial denture fit
- Periodontitis:
- Formation of pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in bite alignment
- Presence of pus between teeth and gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Gum recession or tooth loss
Causes:
- Plaque Buildup: Accumulation of plaque, a bacterial film, on teeth is the primary cause of gum disease. Inadequate removal leads to tartar formation, irritating gums and causing inflammation.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup along the gumline, heightening the risk of gum disease.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking weakens the immune system and blood flow to gums, increasing susceptibility to infection and impeding healing.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can make individuals more susceptible to gum disease, despite good oral hygiene.
- Health Conditions: Systemic diseases like diabetes and autoimmune disorders compromise the body’s ability to fight infections and heal tissues, increasing gum disease risk.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can impact gum health, making women more vulnerable to gum disease.
Prevention:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent buildup.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule routine dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor oral health and detect gum disease signs early.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoid tobacco and maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support oral and overall health.
- Manage Stress: Stress weakens the immune system and increases inflammation, affecting gum health. Practice stress-reduction techniques like exercise and meditation.
- Monitor Hormonal Changes: Be mindful of hormonal fluctuations and maintain good oral hygiene during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
- Seek Prompt Treatment: Consult a dentist if you notice signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath. Early intervention can prevent disease progression.
In conclusion, gum disease is preventable and manageable with good oral hygiene, healthy habits, and timely dental care. By adopting preventive measures and seeking prompt treatment, individuals can maintain healthy gums and a radiant smile.
Contact Information: Phone: +91-92568-92568
Address: 11-12-13-14 H.I.G Market, Opposite Water Tank, Ludhiana, Punjab 141010
Website: https://thind.com

 Timings
Timings